fungi life cycle explained
Ad Free Shipping Available. But this model provides a good overview in terms of how fungi grows from birth to death.

24 3b Zygomycota The Conjugated Fungi Biology Libretexts
But this model provides a good overview in terms of how fungi grows from birth to death.

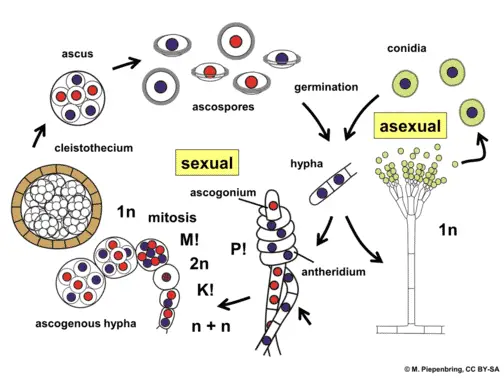
. During the anamorphic stage the fungus is able to reproduce asexually. This fungus has a dimorphic life cycle with yeast and hyphal stages. These hyphae absorb nutrients from the environment allowing the fungi to thrive.
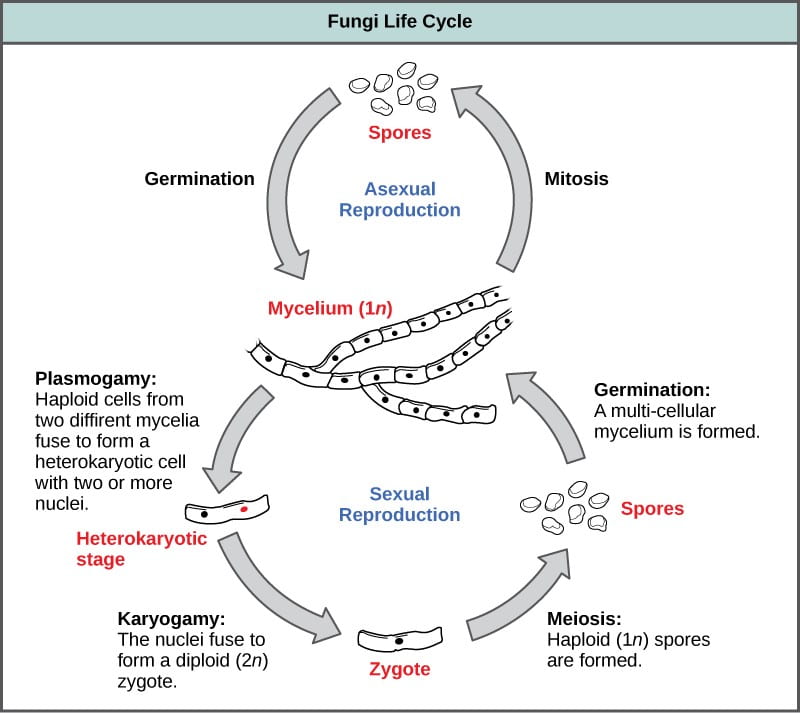
While some fungi reproduce sexually others reproduce asexually. This is when branches of fungi fibre called hyphae start to grow from the spores. They exhibit the phenomenon of alternation of generation.
Great yeast bud scars and pseudohyphae. In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of taphrina explained with the help of suitable diagrams. The term inoculation refers to the spores landing upon and infiltrating a growth medium sometimes known as a substrate.
Time which could partially explain Santas association with flying reindeer. Fungi are eukaryotic non-vascular non-motile and heterotrophic organisms. It is defined by the organisms ability to reproduce sexually.
In this guide we explain the key features of some common mushrooms and provide a brief overview of the fungi life cycle. They are eukaryotic non-vascular non-motile and heterotrophic organisms. Many fungi need two of these colonies to grow next to each other and to mate before that fungus is able to form any new spores and so spread further.
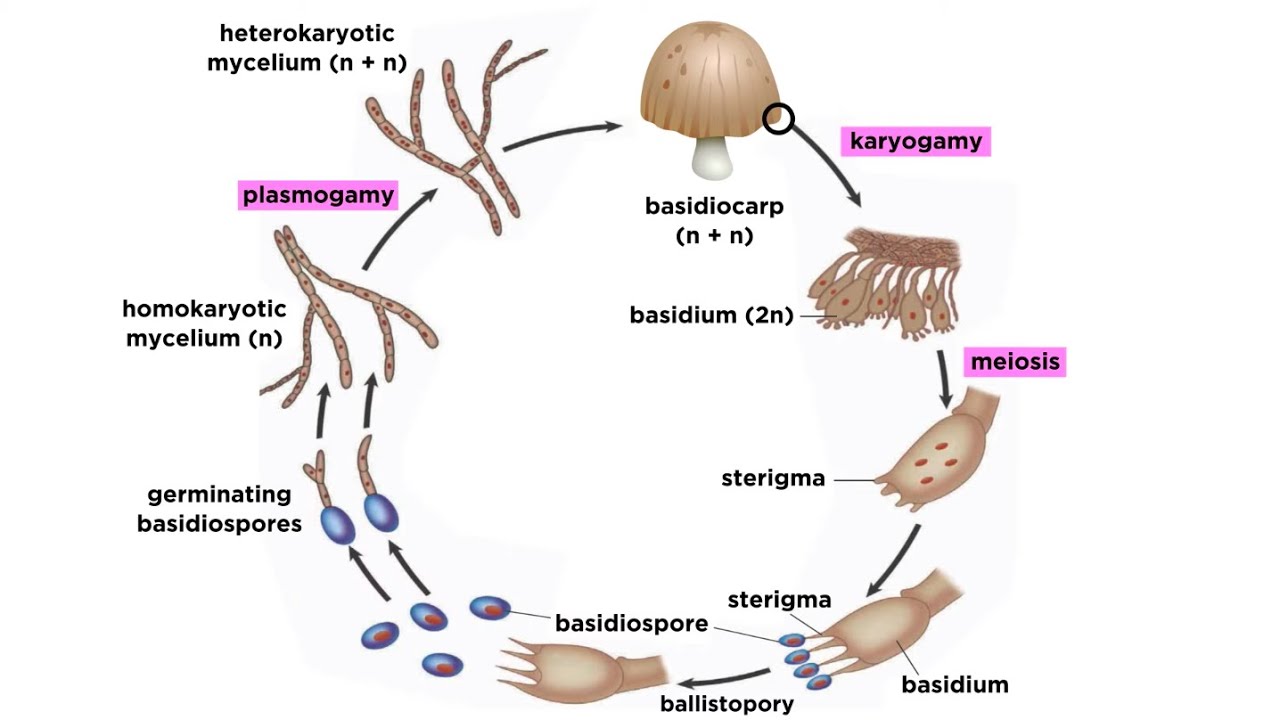
There are four basic steps in the life cycle of a fungi. The life cycle of a fungus is divided into two parts called anamorphic and teleomorphic stages. The life cycle of a mushroom begins and ends through five stages of evolutionary phases beginning as a fungal spore seeds and completing its cycle as a mature fruiting body the part of a mushroom we all identify and know that releases new spores to create a new cycle all over again.
They lack chlorophyll and thus are incapable of photosynthesis. The stage during which a fungus reproduces asexually is known as asexual stage or asexual cycle or conidial stage or imperfect stage. Most of the ecology of the soil will die the plants do ok in the short run as they are able to absorb from the dead bacteria and fungi but it is a slow cycle of death.
There are four basic steps in the life cycle of a fungi. The teleomorphic stage is known as the fruiting stage. Life Cycle of Fungi Some of the characteristic features of fungi are.
Ad Browse Discover Thousands of Book Titles for Less. When they land on favourable conditions they begin to grow germinate and we move on to the next phase Stage 2. When referring to a fungus including both of these stages.
Life Cycle of Fungi. Fungi life cycle explained Wednesday March 2 2022 Edit. They may be unicellular or filamentous.
Edible and Poisonous Fungi Edible fungi Field mushrooms truffles honey rot Poisonous fungi Death Cap destroying angel. If this is a. Mature mycelium In reality there are many sub-steps of the process.
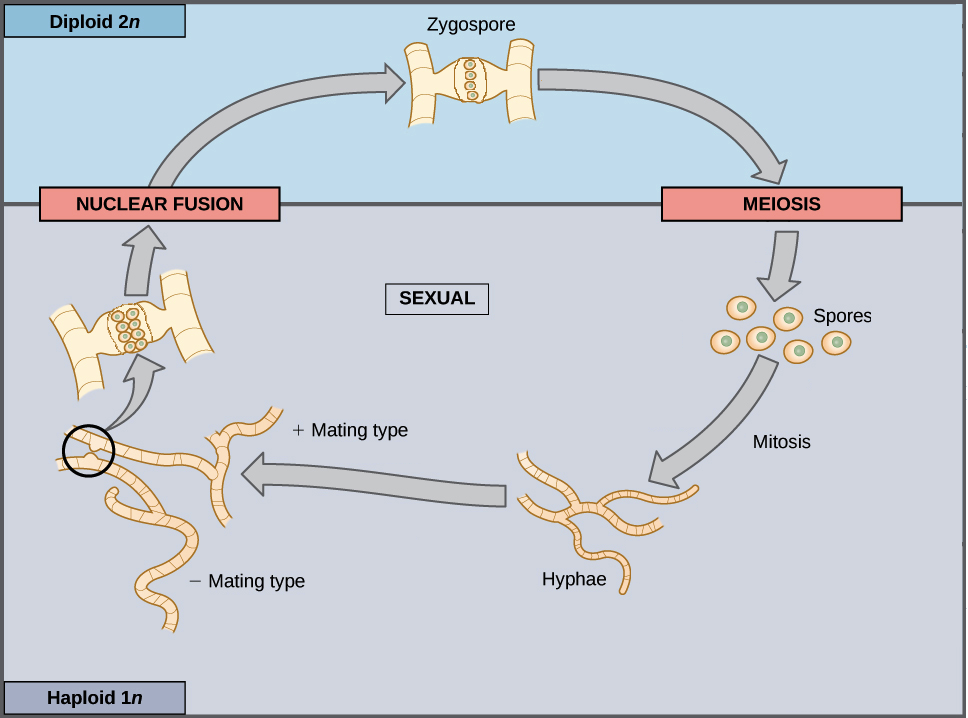
Life Cycle of Rhizopus. Fungi replicate sexually andor asexually. Brundrett 1990 showed the same cycle pattern using an alternative diagram of the developmental stages of a mould.
They reproduce by means of spores. Fungi reproduce sexually either through cross- or self-fertilization. Under favourable climatic conditions the asexual stage may be repeated resulting in the production of conidia in profuse quantities.
The haploid phase ends with nuclear fusion and the diploid phase begins with the formation of the zygote the diploid cell resulting from fusion of two haploid sex cells. Some fungal colonies can grow for a very long time and over a very large area. The genus Taphrina old generic name Exoascus still in use by many authors contains several species which are very important pathogens.
The mushroom life span varies between fungi species. Fungi store their food in the form of starch. The yeast produces hyphae strands and pseudohyphae.
The life cycle inventory phase involves the compilation of elementary flow data ie flows that pass. The organism is haploid and has no diploid phase except for the sexual sporangium. Life cycle of fungi In the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase.
Hyphae Say hi to hyphae. The pseudohyphae can give rise to yeast cells by apical or. A yeast-like fungus commonly occurring on human skin in the upper respiratory alimentary and female genital tracts.
We have summarized them in the fungi life cycle diagram below. They induce hypertrophic malformations of buds leaves twigs flowers and fruits producing. Fungi need to produce so many spores because most spores simply die where they land lacking water and food.
Fungi Explained Here Is What You Need To Know Microscope Clarity

Life Cycle Of An Am Fungus And The Different Steps During Am Development Download Scientific Diagram

Mushroom Life Cycle Kidspressmagazine Com Stuffed Mushrooms Life Cycles Science For Kids

Life Cycle Of Aspergillus And Suggested Localization Of Ribotoxins Download Scientific Diagram

Diagrammatic Representation Of Mushroom Life Cycle Download Scientific Diagram
Sexual Life Cycles Article Meiosis Khan Academy

Life Cycle Of A Mushroom Worldkids

Reproduction In Fungi Life Cycle Of Fungi Youtube

A Detailed Explanation Of The Mushroom Life Cycle Grocycle

Ascomycota The Sac Fungi Biology For Majors Ii

24 1c Fungi Reproduction Biology Libretexts

Plasmogamy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Biology Pictures Fungi Life Cycle 3 Life Cycles Fungi Biology